本文最后更新于 2025-01-10T22:20:34+08:00
说明:
- 本文档由DuRuofu撰写,由DuRuofu负责解释及执行。
- 本文档主要介绍ESP32的FAT (虚拟文件系统)
修订历史:
| 文档名称 |
版本 |
作者 |
时间 |
备注 |
| ESP32存储-FAT 文件系统 |
v1.0.0 |
DuRuofu |
2024-03-06 |
首次建立 |
ESP32存储-VFS虚拟文件系统
一、介绍
1.1 什么是VFS
虚拟文件系统的作用是:使得计算机上层的软件,能够用单一的方式,来跟底层不同的文件系统沟通(无论是真实的文件系统还是虚拟的文件系统)。在操作系统与之下的各种文件系统之间,虚拟文件系统提供了标准的操作接口,将所有不同种类的文件系统统一起来。
我们常说”Linux下一切皆文件“,指的就是Linux通过VFS把一切设备都抽象成一个统一的文件系统,从设备读取数据视为向“文件”读取数据,向设备发送数据视为写数据到“文件”。并且不同的“文件”之间读写方式相同。
Linux这时候不再需要关注这个设备具体读写方式的区别,而直接使用相同的高层操作完成与外设的数据交互。
1.2 ESP32的VFS
ESP32借助这种概念,设计了虚拟文件系统 (VFS) 组件,为驱动程序提供一个统一接口,可以操作类文件对象。这类驱动程序可以是 FAT、SPIFFS 等真实文件系统,也可以是提供文件类接口的设备驱动程序。
ESP32的VFS支持fprintf fopen等标准C库函数,调用这个函数本质上就是对VFS的访问。并提供了“路径”“文件描述符”等概念。不同的文件系统通过文件路劲来区分。
如,可以使用 /fat 前缀注册 FAT 文件系统驱动程序,并调用 fopen(“/fat/file.txt”,“w”)。然后,VFS 组件将调用 FAT 驱动程序的 open 函数并将 /file.txt 参数传递给它(以及适当的模式标志)。对返回的 FILE * 流的所有后续 C 库函数调用也将被转发到 FAT 驱动程序。
对于VFS,我们可以通过手动实现读与写来挂载文件系统。除此之外,ESP-IDF提供了大量简化API为开发者实现了挂载常用的文件系统,如:
- 挂载ESP32或模组内部
flash为Fat文件系统
- 挂载SD卡为
Fat文件系统
- ·······
1.2.1 VFS的挂载点和路径
一个标准ESP32 VFS路径如下所示
上面的示例包含了“挂载点”和“路径”
- 挂载点名称必须以路径分隔符 (
/) 开头,且分隔符后至少包含一个字符,一个挂载点被认为成一个文件系统,/不是根文件系统。
- VFS允许多层挂载点,可以将
/storage/sdcard作为挂载点
1.2.2 文件描述符
文件描述符是一组很小的正整数,从 0 到 FD_SETSIZE - 1,FD_SETSIZE 定义在 sys/select.h。最大文件描述符由 CONFIG_LWIP_MAX_SOCKETS 定义,且为套接字保留。VFS 中包含一个名为 s_fd_table 的查找表,用于将全局文件描述符映射至 s_vfs 数组中注册的 VFS 驱动索引。
1.2.3 标准IO流: stdin、stdout、stderr
如果 menuconfig 中 UART for console output 选项没有设置为 None,则 stdin、 stdout 和 stderr 将默认从 UART 读取或写入。UART0 或 UART1 可用作标准 IO。默认情况下,UART0 使用 115200 波特率,TX 管脚为 GPIO1,RX 管脚为 GPIO3。上述参数可以在 menuconfig 中更改。
二、使用VFS虚拟文件系统( FatFs)
将内部flash挂载为Fat文件系统
2.1 新建工程,准备自定义分区表
在分区表里添加 fat 文件系统的分区
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # ESP-IDF Partition Table
# Name, Type, SubType, Offset, Size, Flags
nvs, data, nvs, 0x9000, 0x4000,
phy_init, data, phy, 0xf000, 0x1000,
factory, app, factory, 0x10000, 1M,
storage, data, fat, 0x110000, 1M,
|
选择自定义分区表:
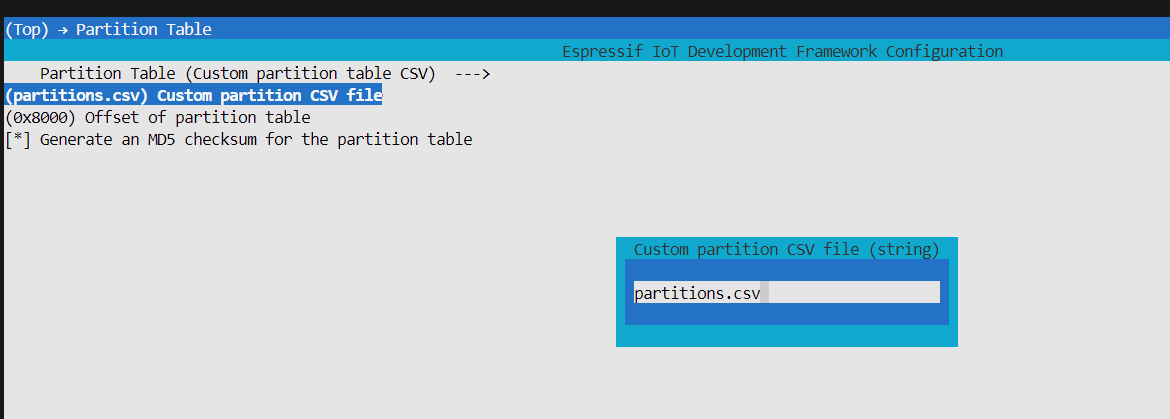
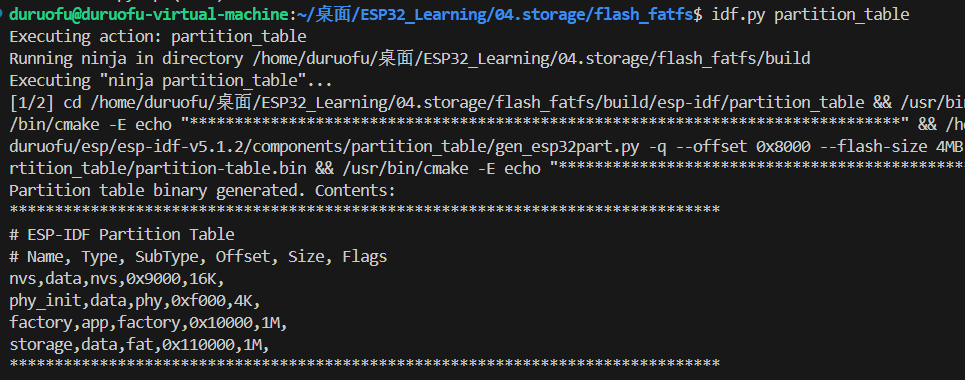
配置好可以使用idf.py partition_table生成二进制分区表
2.2 挂载文件系统
使用esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_mount_rw_wl()在SPI闪存中初始化FAT文件系统并在VFS中注册。
- base_path: FATFS 分区应该挂载的路径(例如 “/spiflash”)。
- partition_label: 应该使用的分区标签。
- mount_config: 针对挂载 FATFS 的额外参数结构体指针。
- wl_handle: [输出] 磨损平衡驱动程序句柄。
返回值:
- ESP_OK: 成功。
- ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: 如果分区表中不包含具有给定标签的 FATFS 分区。
- ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: 如果已经调用了 esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_mount_rw_wl。
- ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: 如果无法分配内存。
- ESP_FAIL: 如果无法挂载分区。
mount_config是一个针对挂载 FATFS 的额外参数配置结构体,原形为esp_vfs_fat_mount_config_t,参数如下:
- format_if_mount_failed: 如果 FAT 分区无法挂载,且此参数为 true,则创建分区表并格式化文件系统。
- max_files: 最大打开文件数。
- allocation_unit_size: 如果设置了 format_if_mount_failed 并且挂载失败,使用给定的分配单元大小格式化卡。必须是2的幂,在扇区大小和128*扇区大小之间。对于 SD 卡,扇区大小始终为512字节。对于磨损平衡,扇区大小由 CONFIG_WL_SECTOR_SIZE 选项确定。使用较大的分配单元大小将导致更高的读/写性能和在存储小文件时更高的开销。
- disk_status_check_enable: 启用真实的 ff_disk_status 函数实现以用于 SD 卡(ff_sdmmc_status)。可能会降低 IO 性能。如果需要处理 SD 卡未正确卸载就物理移除或者遇到 SD 卡问题的情况,请尝试启用。对于其他存储介质则不起作用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
static bool mount_fatfs(const char* partition_label)
{
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Mounting FAT filesystem");
const esp_vfs_fat_mount_config_t mount_config = {
.max_files = 4,
.format_if_mount_failed = true,
.allocation_unit_size = CONFIG_WL_SECTOR_SIZE
};
esp_err_t err = esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_mount_rw_wl(base_path, partition_label, &mount_config, &s_wl_handle);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to mount FATFS (%s)", esp_err_to_name(err));
return false;
}
return true;
}
|
使用标准C库读写文件
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Opening file");
FILE *f = fopen("/flash/hello.txt", "wb");
if (f == NULL) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to open file for writing");
return;
}
fprintf(f, "fat文件系统测试 %s\n", "hollo world!");
fclose(f);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "File written");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Reading file");
f = fopen("/flash/hello.txt", "rb");
if (f == NULL) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to open file for reading");
return;
}
char line[128];
fgets(line, sizeof(line), f);
fclose(f);
char *pos = strchr(line, '\n');
if (pos) {
*pos = '\0';
}
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Read from file: '%s'", line);
|
fopen 函数:用于打开一个文件,并返回一个指向该文件的文件指针。在这段代码中,它被用于打开 “/flash/hello.txt” 文件,以便进行写入和读取操作。第二个参数 “wb” 表示以写入模式打开文件,”rb” 表示以读取模式打开文件。
fprintf 函数:用于把格式化的数据写入文件中。在这段代码中,它被用于向文件中写入一行格式化的文本内容。
fclose 函数:用于关闭先前通过 fopen 打开的文件。在这段代码中,它被用于关闭文件句柄,确保文件被正确地写入到存储介质中。
fgets 函数:用于从文件中读取一行数据。在这段代码中,它被用于读取 “/flash/hello.txt” 文件中的内容。
卸载文件系统
1
2
3
4
5
6
| ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Unmounting FAT filesystem");
esp_err_t unmount_err = esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_unmount_rw_wl(base_path, s_wl_handle);
if (unmount_err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to unmount FATFS (%s)", esp_err_to_name(unmount_err));
return;
}
|
三、示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
|
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "esp_flash.h"
#include "esp_vfs.h"
#include "esp_vfs_fat.h"
#include "esp_system.h"
static const char *TAG = "FAT";
static wl_handle_t s_wl_handle = WL_INVALID_HANDLE;
const char *base_path = "/flash";
static bool mount_fatfs(const char* partition_label)
{
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Mounting FAT filesystem");
const esp_vfs_fat_mount_config_t mount_config = {
.max_files = 4,
.format_if_mount_failed = true,
.allocation_unit_size = CONFIG_WL_SECTOR_SIZE
};
esp_err_t err = esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_mount_rw_wl(base_path, partition_label, &mount_config, &s_wl_handle);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to mount FATFS (%s)", esp_err_to_name(err));
return false;
}
return true;
}
void app_main(void)
{
const char *partition_label = "storage";
if (!mount_fatfs(partition_label)) {
return;
}
uint64_t bytes_total, bytes_free;
esp_vfs_fat_info(base_path, &bytes_total, &bytes_free);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "FAT FS: %" PRIu64 " kB total, %" PRIu64 " kB free", bytes_total / 1024, bytes_free / 1024);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Opening file");
FILE *f = fopen("/flash/hello.txt", "wb");
if (f == NULL) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to open file for writing");
return;
}
fprintf(f, "fat文件系统测试 %s\n", "hollo world!");
fclose(f);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "File written");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Reading file");
f = fopen("/flash/hello.txt", "rb");
if (f == NULL) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to open file for reading");
return;
}
char line[128];
fgets(line, sizeof(line), f);
fclose(f);
char *pos = strchr(line, '\n');
if (pos) {
*pos = '\0';
}
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Read from file: '%s'", line);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Unmounting FAT filesystem");
esp_err_t unmount_err = esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_unmount_rw_wl(base_path, s_wl_handle);
if (unmount_err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to unmount FATFS (%s)", esp_err_to_name(unmount_err));
return;
}
}
|
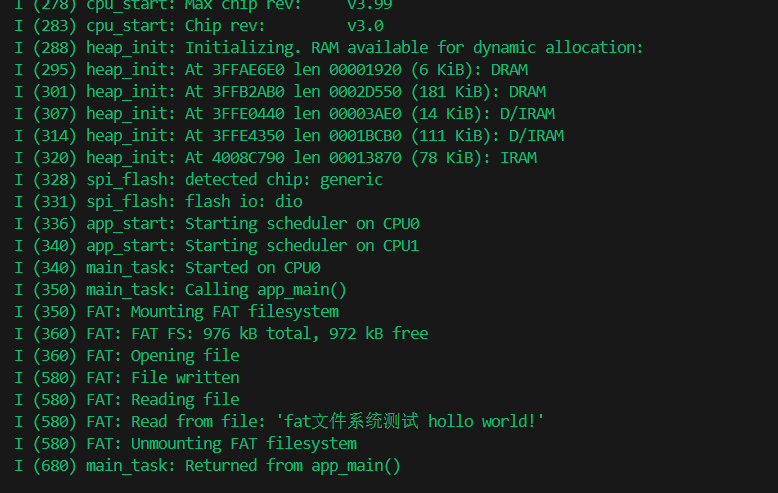
效果:
四、补充:从本地文件创建 FATFS 文件系统映像
可以使用FatFs 分区生成器工具:
通过调用 fatfs_create_partition_image 可以直接从 CMake 构建系统中调用 FatFs 分区生成器:
1
| fatfs_create_spiflash_image(<partition> <base_dir> [FLASH_IN_PROJECT])
|
参考:
- https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/zh_CN/stable/esp32/api-reference/storage/fatfs.html
- https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf/tree/v5.2.1/examples/storage/fatfsgen
根目录新建一个fatfs_image目录存放我们的文件镜像,
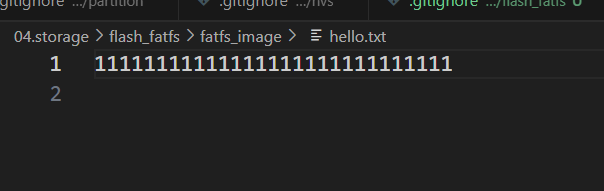
新建hello.txt 写上内容
然后在下面main组件的CMakeLists文件添加:
1
2
3
4
5
| idf_component_register(SRCS "flash_fatfs.c"
INCLUDE_DIRS ".")
set(image ../fatfs_image)
fatfs_create_spiflash_image(storage ${image} FLASH_IN_PROJECT)
|
然后修改主程序:
尝试读取刚才烧录的文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "esp_flash.h"
#include "esp_vfs.h"
#include "esp_vfs_fat.h"
#include "esp_system.h"
static const char *TAG = "FAT";
static wl_handle_t s_wl_handle = WL_INVALID_HANDLE;
const char *base_path = "/fatfs_image";
static bool mount_fatfs(const char* partition_label)
{
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Mounting FAT filesystem");
const esp_vfs_fat_mount_config_t mount_config = {
.max_files = 4,
.format_if_mount_failed = true,
.allocation_unit_size = CONFIG_WL_SECTOR_SIZE
};
esp_err_t err = esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_mount_rw_wl(base_path, partition_label, &mount_config, &s_wl_handle);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to mount FATFS (%s)", esp_err_to_name(err));
return false;
}
return true;
}
void app_main(void)
{
const char *partition_label = "storage";
if (!mount_fatfs(partition_label)) {
return;
}
uint64_t bytes_total, bytes_free;
esp_vfs_fat_info(base_path, &bytes_total, &bytes_free);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "FAT FS: %" PRIu64 " kB total, %" PRIu64 " kB free", bytes_total / 1024, bytes_free / 1024);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Reading file");
FILE *f = fopen("/fatfs_image/hello.txt", "rb");
if (f == NULL) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to open file for reading");
return;
}
char line[128];
fgets(line, sizeof(line), f);
fclose(f);
char *pos = strchr(line, '\n');
if (pos) {
*pos = '\0';
}
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Read from file: '%s'", line);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Unmounting FAT filesystem");
esp_err_t unmount_err = esp_vfs_fat_spiflash_unmount_rw_wl(base_path, s_wl_handle);
if (unmount_err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to unmount FATFS (%s)", esp_err_to_name(unmount_err));
return;
}
}
|
参考链接
- https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/zh_CN/release-v5.2/esp32/api-reference/storage/vfs.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51518255/article/details/112253634
- https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf/tree/v5.2.1/examples/storage/fatfsgen



